Passive Design Examples
Example 1 - Potential Divider
Design a potential divider with a gain of 0.65. The Schematic is shown below.
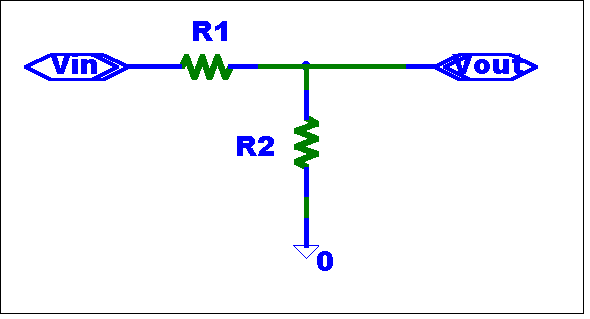
Legacy Analysis:
R2 / (R1 + R2) = 0.65
Let (R1 + R2) = 1k for simplicity
R2 = 650
R1 = 1k – 650 =350
K9 Analysis:
G0 = 1 – 0.65 = 0.35
Let ZPout = 1k
R1 = 1k / 0.65 = 1.5385k
R2 = 1k /0.35 = 2.857k
1.5385k // 2.857k = 1k
The design complexity is about equal. You pick the preferred method.
Example 2 - Passive Summing Circuit
Design a passive summing circuit with gains of 0.1, 0.25, and 0.4.
V(out) = 0.1 * V1 + 0.25 * V2 + 0.45 * V3
The schematic is shown below.
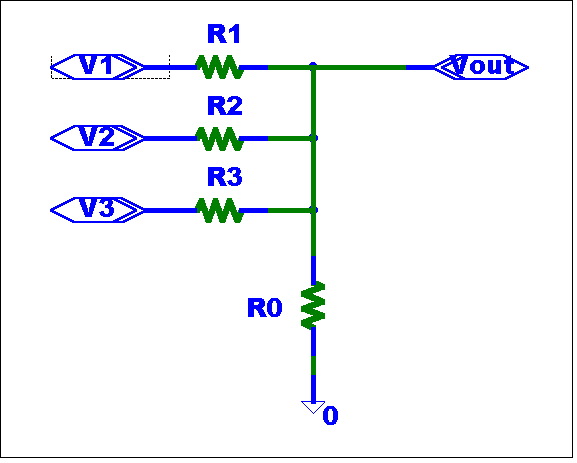
Legacy Analysis:
Write the potential divider equations.
(R2 // R3 // R0) / (R1 + (R2 // R3 // R0 )) = 0.1
(R1 // R3 // R0) / (R2 + (R1 // R3 // R0 )) = 0.25
(R1 // R2 // R0) / (R3 + (R1 // R2 // R0 )) = 0.45
Solve the equations.
This is left as a reader exercise. Far too complicated for K9 Analysis.
K9 Analysis:
G0 = 1 – (0.1 + 0.25 + 0.45) = 0.2
Let ZPout = 1k
R1 = 1k / 0.1 = 10k
R2 = 1k / 0.25 = 4k
R3 = 1k / 0.45 = 2.22k
R0 = 1k / 0.2 = 5k
10k // 4k // 2.22k // 5k = 1k
With Legacy Analysis the equations are difficult to solve. Passive Summing Circuit with 2 or more inputs are rarely used due to the design complexity.
The K9 Design Procedure is Simple for all cases.